Microsoft Eases AI Testing with New Red Teaming Tool
Plus: Transformers learn to plan better with Searchformer, YOLOv9 sets a new standard for real-time object recognition
Hello, Engineering Leaders and AI Enthusiasts!
Welcome to the 218th edition of The AI Edge newsletter. This edition brings you details on Microsoft’s first GenAI red teaming automation tool - PyRIT.
And a huge shoutout to our amazing readers. We appreciate you😊
In today’s edition:
🛡️Microsoft eases AI testing with new red teaming tool
🧠 Transformers learn to plan better with Searchformer
👀 YOLOv9 sets a new standard for real-time object recognition
📚 Knowledge Nugget: Generative AI is good at cooperating with people and bad at full automation by skybrian
Let’s go!
Microsoft eases AI testing with new red teaming tool
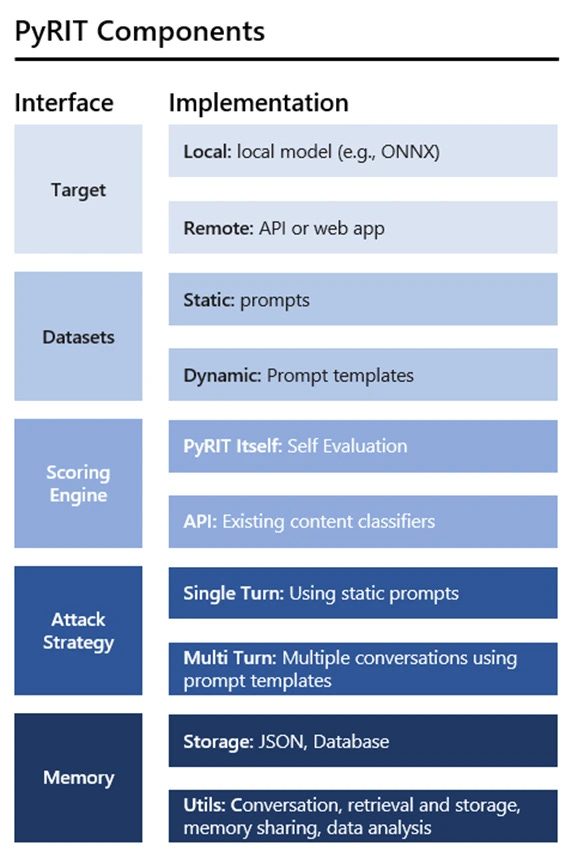
Microsoft has released an open-source automation toolkit called PyRIT to help security researchers test for risks in generative AI systems before public launch. Historically, "red teaming" AI has been an expert-driven manual process requiring security teams to create edge case inputs and assess whether the system's responses contain security, fairness, or accuracy issues. PyRIT aims to automate parts of this tedious process for scale.
PyRIT helps researchers test AI systems by inputting large datasets of prompts across different risk categories. It automatically interacts with these systems, scoring each response to quantify failures. This allows for efficient testing of thousands of input variations that could cause harm. Security teams can then take this evidence to improve the systems before release.
Why does this matter?
Microsoft's release of the PyRIT toolkit makes rigorously testing AI systems for risks drastically more scalable. Automating parts of the red teaming process will enable much wider scrutiny for generative models and eventually raise their performance standards. PyRIT's automation will also pressure the entire industry to step up evaluations if they want their AI trusted.
Transformers learn to plan better with Searchformer
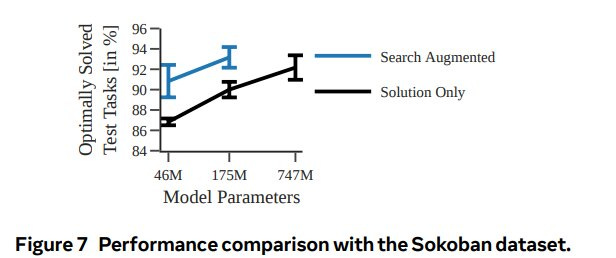
A new paper from Meta introduces Searchformer, a Transformer model that exceeds the performance of traditional algorithms like A* search in complex planning tasks such as maze navigation and Sokoban puzzles. Searchformer is trained in two phases: first imitating A* search to learn general planning skills, then fine-tuning the model via expert iteration to find optimal solutions more efficiently.
The key innovation is the use of search-augmented training data that provides Searchformer with both the execution trace and final solution for each planning task. This enables more data-efficient learning compared to models that only see solutions. However, encoding the full reasoning trace substantially increases the length of training sequences. Still, Searchformer shows promising techniques for training AI to surpass symbolic planning algorithms.
Why does this matter?
Achieving state-of-the-art planning results shows that generative AI systems are advancing to develop human-like reasoning abilities. Mastering complex cognitive tasks like finding optimal paths has huge potential in AI applications that depend on strategic thinking and foresight. As other companies race to close this new gap in planning capabilities, progress in core areas like robotics and autonomy is likely to accelerate.
YOLOv9 sets a new standard for real-time object recognition
YOLO (You Only Look Once) is open-source software that enables real-time object recognition in images, allowing machines to “see” like humans. Researchers have launched YOLOv9, the latest iteration that achieves state-of-the-art accuracy with significantly less computational cost.
By introducing two new techniques, Programmable Gradient Information (PGI) and Generalized Efficient Layer Aggregation Network (GELAN), YOLOv9 reduces parameters by 49% and computations by 43% versus predecessor YOLOv8, while boosting accuracy on key benchmarks by 0.6%. PGI improves network updating for more precise object recognition, while GELAN optimizes the architecture to increase accuracy and speed.
Why does this matter?
The advanced responsiveness of YOLOv9 unlocks possibilities for mobile vision applications where computing resources are limited, like drones or smart glasses. More broadly, it highlights deep learning's potential to match human-level visual processing speeds, encouraging technology advancements like self-driving vehicles.
Enjoying the daily updates?
Refer your pals to subscribe to our daily newsletter and get exclusive access to 400+ game-changing AI tools.
When you use the referral link above or the “Share” button on any post, you'll get the credit for any new subscribers. All you need to do is send the link via text or email or share it on social media with friends.
Knowledge Nugget: Generative AI is good at cooperating with people and bad at full automation
In his insightful piece, skybrian explores how generative AI models have very different strengths compared to traditional software. He notes that tools like image generators and chatbots thrive on providing random variety, making them engaging and fun for interactive use. However, their unpredictability makes them poor at repetitive automation tasks requiring consistency, like running factory assembly lines.
He suggests that the ideal approach is to combine the complementary strengths of both generative AI and software. We should aim for a future where people collaborate interactively with AI tools to develop programs and scripts. Then, once finalized, these scripts can be reliably executed repeatedly by software without human oversight. In essence. there is tremendous promise in human-AI cooperation, with people leveraging AI's creative abilities and software delivering scalable, efficient automation.
Why does this matter?
As the adoption of generative AI grows, properly distinguishing its capabilities from traditional code is important. Misapplying unpredictable models risks operational problems and inefficiencies. But failing to leverage their creative potential results in losing out on innovations, too. Companies navigating this balance correctly will pioneer the most fruitful human-AI collaboration. Those who don't may deploy flawed integrations.
What Else Is Happening❗
🍎Apple tests internal ChatGPT-like tool for customer support
Apple recently launched a pilot program testing an internal AI tool named "Ask." It allows AppleCare agents to generate technical support answers automatically by querying Apple's knowledge base. The goal is faster and more efficient customer service. (Link)
📱 ChatGPT gets an Android home screen widget
Android users can now access ChatGPT more easily through a home screen widget that provides quick access to the chatbot's conversation and query modes. The widget is available in the latest beta version of the ChatGPT mobile app. (Link)
🤖 AWS adds open-source Mistral AI models to Amazon Bedrock
AWS announced it will be bringing two of Mistral's high-performing generative AI models, Mistral 7B and Mixtral 8x7B, to its Amazon Bedrock platform for GenAI offerings in the near future. AWS chose Mistral's cost-efficient and customizable models to expand the range of GenAI abilities for Bedrock users. (Link)
🚇 Montreal tests AI system to prevent subway suicides
The Montreal Transit Authority is testing an AI system that analyzes surveillance footage to detect warning signs of suicide risk among passengers. The system, developed with a local suicide prevention center, can alert staff to intervene and save lives. With current accuracy of 25%, the "promising" pilot could be implemented in two years. (Link)
🍔 Fast food giants embrace controversial AI worker tracking
Riley, an AI system by Hoptix, monitors worker-customer interactions in 100+ fast-food franchises to incentivize upselling. It tracks metrics like service speed, food waste, and upselling rates. Despite being a coaching tool, concerns exist regarding the imposition of unfair expectations on workers. (Link)
New to the newsletter?
The AI Edge keeps engineering leaders & AI enthusiasts like you on the cutting edge of AI. From machine learning to ChatGPT to generative AI and large language models, we break down the latest AI developments and how you can apply them in your work.
Thanks for reading, and see you tomorrow. 😊