Build Resource-Efficient LLMs with Google's MoD
Plus: Newton brings sensor-driven intelligence to AI models, Internet archives become AI training goldmines as tech titans spend big
Hello Engineering Leaders and AI Enthusiasts!
Welcome to the 248th edition of The AI Edge newsletter. This edition brings you details on Google’s MoD, a method to allocate compute resources in LLMs intelligently.
And a huge shoutout to our incredible readers. We appreciate you😊
In today’s edition:
⚖️ Build resource-efficient LLMs with Google’s MoD
📡 Newton brings sensor-driven intelligence to AI models
💰 Internet archives become AI training goldmines for Big Tech
💡 Knowledge Nugget: Building LLM application using RAG by
Let’s go!
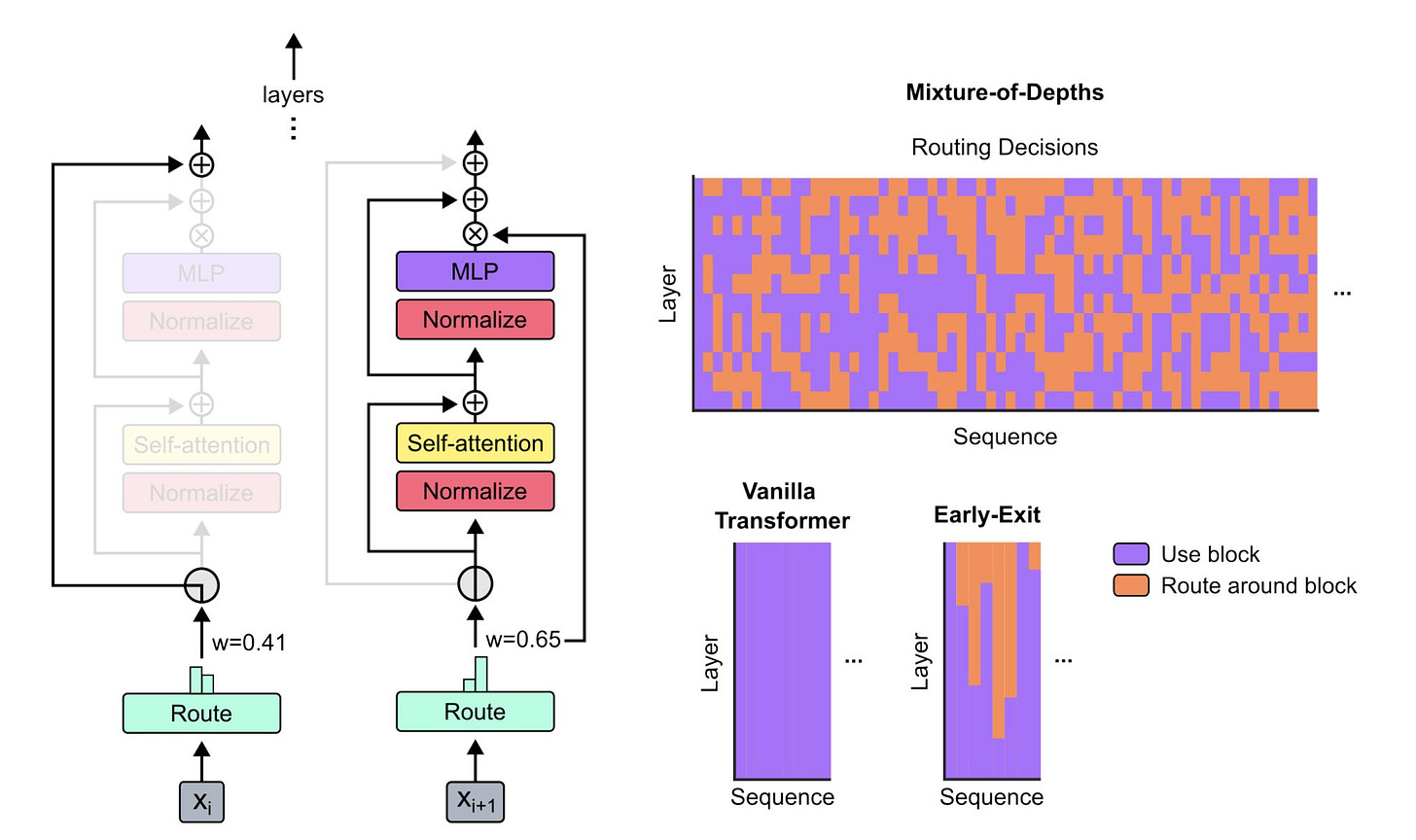
Build resource-efficient LLMs with Google's MoD
Google DeepMind has introduced "Mixture-of-Depths" (MoD), an innovative method that significantly improves the efficiency of transformer-based language models. Unlike traditional transformers that allocate the same amount of computation to each input token, MoD employs a "router" mechanism within each block to assign importance weights to tokens. This allows the model to strategically allocate computational resources, focusing on high-priority tokens while minimally processing or skipping less important ones.
Notably, MoD can be integrated with Mixture-of-Experts (MoE), creating a powerful combination called Mixture-of-Depths-and-Experts (MoDE). Experiments have shown that MoD transformers can maintain competitive performance while reducing computational costs by up to 50% and achieving significant speedups during inference.
Why does this matter?
MoD can greatly reduce training times and enhance model performance by dynamically optimizing computational resources. Moreover, it adapts the model's depth based on the complexity of the task at hand. For simpler tasks, it employs shallower layers, conserving resources. Conversely, for intricate tasks, it deepens the network, enhancing representation capacity. This adaptability ensures that creators can fine-tune LLMs for specific use cases without unnecessary complexity.
Newton brings sensor-driven intelligence to AI models
Startup Archetype AI has launched with the ambitious goal of making the physical world understandable to artificial intelligence. By processing data from a wide variety of sensors, Archetype's foundational AI model called Newton aims to act as a translation layer between humans and the complex data generated by the physical world.
Using plain language, Newton will allow people to ask questions and get insights about what's happening in a building, factory, vehicle, or even the human body based on real-time sensor data. The company has already begun pilot projects with Amazon, Volkswagen, and healthcare researchers to optimize logistics, enable smart vehicle features, and track post-surgical recovery. Archetype's leadership team brings deep expertise from Google's Advanced Technology and Products (ATAP) division.
Why does this matter?
General-purpose AI systems like Newton that can interpret diverse sensor data will be the pathway to building more capable, context-aware machines. In the future, users may increasingly interact with AI not just through screens and speakers but through intelligently responsive environments that anticipate and adapt to their needs. However, as AI becomes more deeply embedded in the physical world, the stakes of system failures or unintended consequences become higher.
Internet archives become AI training goldmines for Big Tech
To gain an edge in the heated AI arms race, tech giants Google, Meta, Microsoft, and OpenAI are spending billions to acquire massive datasets for training their AI models. They are turning to veteran internet companies like Photobucket, Shutterstock, and Freepik, who have amassed vast archives of images, videos, and text over decades online.
The prices for this data vary depending on the type and buyer but range from 5 cents to $7 per image, over $1 per video, and around $0.001 per word for text. The demand is so high that some companies are requesting billions of videos, and Photobucket says it can't keep up.
Why does this matter?
This billion-dollar rush for AI training data could further solidify Big Tech's dominance in artificial intelligence. As these giants hoard the data that's crucial for building advanced AI models, it may become increasingly difficult for startups or academic labs to compete on a level playing field. We need measures to protect the future diversity and accessibility of AI technologies.
Enjoying the daily updates?
Refer your pals to subscribe to our daily newsletter and get exclusive access to 400+ game-changing AI tools.
When you use the referral link above or the “Share” button on any post, you'll get the credit for any new subscribers. All you need to do is send the link via text or email or share it on social media with friends.
Knowledge Nugget: Building an LLM application using RAG
In his recent article,
discusses Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG), a powerful technique that addresses the limitations of LLMs by grounding them in custom knowledge bases. RAG allows organizations to deploy LLMs that provide accurate, domain-specific responses without the need for extensive fine-tuning or pre-training.Gandhi outlines a simple 5-step process for building an LLM application using RAG, which includes document loading and splitting, embedding creation, vector store indexing, LLM definition, and the retrieval-augmentation-generation pipeline. The article also explores practical applications of RAG, such as enhancing chatbots, augmenting search results, and creating internal knowledge engines for easy access to company-specific information.
Why does this matter?
While the concept of RAG has been around for some time, its importance has grown recently due to the rapid advancements in LLMs. By enabling LLMs to access and incorporate up-to-date, domain-specific information, RAG effectively addresses the issues of knowledge staleness and generalization that have long plagued these models. It also democratizes access to powerful language models by allowing organizations to leverage their own data without the prohibitive costs and time associated with fine-tuning or pre-training.
What Else Is Happening❗
🎧 Spotify introduces AI-generated personalized playlists
Spotify has launched AI-powered personalized playlists that users can create using text prompts. The feature is currently available in beta for UK and Australia users on iOS and Android. Spotify uses LLMs to understand the prompt's intent and its personalization technology to generate a custom playlist, which users can further refine. (Link)
🔍 Meta expands "Made with AI" labeling to more content types
Meta will start applying a "Made with AI" badge to a broader range of AI-generated content, including videos, audio, and images. The company will label content where it detects AI image indicators or when users acknowledge uploading AI-generated content. (Link)
🚀 Gretel's Text-to-SQL dataset sets new standard for AI training data
Gretel has released the world's largest open-source Text-to-SQL dataset containing over 100,000 high-quality synthetic samples spanning 100 verticals. The dataset, generated using Gretel Navigator, aims to help businesses unlock the potential of their data by enabling AI models to understand natural language queries and generate SQL queries. (Link)
💾 Microsoft upgrades Azure AI Search with more storage and support for OpenAI apps
Microsoft has made Azure AI Search more cost-effective for developers by increasing its vector and storage capacity. The service now supports OpenAI applications, including ChatGPT and GPTs, through Microsoft's retrieval augmented generation system. Developers can now scale their apps to a multi-billion vector index within a single search without compromising speed or performance. (Link)
📱 Google brings Gemini AI chatbot to Android app
Google is bringing its AI chatbot, Gemini, to the Android version of the Google app. Similar to its iOS integration, users can access Gemini by tapping its logo at the top of the app, opening a chatbot prompt field. Here, users can type queries, request image generation, or ask for image analysis. (Link)
New to the newsletter?
The AI Edge keeps engineering leaders & AI enthusiasts like you on the cutting edge of AI. From ML to ChatGPT to generative AI and LLMs, We break down the latest AI developments and how you can apply them in your work.
Thanks for reading, and see you tomorrow. 😊



Pretty good explanation of MoD there Rohit! I was just reading this paper yesterday.
Looking forward to your future contents.