Amazon is using AI to improve your holiday shopping
Plus: AI algorithms empowering cell microscopy, AWS gives Amazon Transcribe new languages and capabilities.
Hello Engineering Leaders and AI Enthusiasts!
Welcome to the 156th edition of The AI Edge newsletter. This edition brings you how Amazon is using AI to improve holiday shopping.
And a huge shoutout to our amazing readers. We appreciate you😊
In today’s edition:
🎁 Amazon is using AI to improve your holiday shopping
🧠 AI algorithms are powering the search for cells
🚀 AWS adds new languages and AI capabilities to Amazon Transcribe
📚 Knowledge Nugget: Defensibility in GenAI: What AI Startups can learn from Github Copilot by Dan Nguyen-Huu
Let’s go!
Amazon is using AI to improve your holiday shopping
This holiday season, Amazon is using AI to power and enhance every part of the customer journey. Its new initiatives include:
Supply Chain Optimization Technology (SCOT): It helps forecast demand for more than 400 million products each day, using deep learning and massive datasets to decide which products to stock in which quantities at which Amazon facility.
AI-enabled robots: AI is also helping Amazon orchestrate the world’s largest fleet of mobile industrial robots. They help recognize, sort, inspect, package, and load millions of diverse goods.
A robot called “Robin” helps sort packages for fast delivery: It uses an AI-enhanced vision system to understand what objects are there– different-sized boxes, soft packages, and envelopes on top of each other.
AI helps predict the unpredictable on the road: Whether it's bad weather or traffic, or a truck with products might come to the station early.
Picking the best delivery routes: Route design and optimization is notoriously one of the most difficult problems for Amazon. It uses over 20 ML models that work in concert behind the scenes.
In addition, delivery teams are exploring the use of generative AI and LLMs to simplify decisions for drivers: by clarifying customer delivery notes, building outlines, road entry points, and much more.
Why does this matter?
AI shows up in everything Amazon does, and it had even before the AI boom brought on by ChatGPT. Now, Amazon is actively integrating generative AI into its operations to maximize its utilization.
It shows Amazon’s focus on truly implementing AI for practical use cases in day-to-day business while the world might still be in the experimental phase.
(Source)
AI algorithms are powering the search for cells
Deep learning is driving the rapid evolution of algorithms that can automatically find and trace cells in a wide range of microscopy experiments. New models are reaching unprecedented accuracy heights.
A new paper by Nature details how AI-powered image analysis tools are changing the game for microscopy data. It highlights the evolution from early, labor-intensive methods to machine learning-based tools like CellProfiler, ilastik, and newer frameworks such as U-Net. These advancements enable more accurate and faster segmentation of cells, essential for various biological imaging experiments.
Cancer-cell nuclei (green boxes) picked out by software using deep learning.
Why does this matter?
The short study highlights the potential for AI-driven tools to revolutionize further biological analyses. The advancement is crucial for understanding diseases, drug development, and gaining insights into cellular behavior, enabling faster scientific discoveries in various fields like medicine and biology.
AWS adds new languages and AI capabilities to Amazon Transcribe
As announced during AWS re:Invent, the cloud provider added new languages and a slew of new AI capabilities to Amazon Transcribe. The product will now offer generative AI-based transcription for 100 languages. AWS ensured that some languages were not over-represented in the training data to ensure that lesser-used languages could be as accurate as more frequently spoken ones.
It also offers automatic punctuation, custom vocabulary, automatic language identification, and custom vocabulary filters. It can recognize speech in audio and video formats and noisy environments.
Why does this matter?
This leads to better capabilities for customers’ apps on the AWS Cloud and better accuracy in its Call Analytics platform, which contact center customers often use.
Of course, AWS is not the only one offering AI-powered transcription services. Otter provides AI transcriptions to enterprises and Meta is working on a similar model. But AWS has edge because having Transcribe within its suite of services ensures compatibility and eliminates the hassle of integrating disparate systems, enable customers to build innovative solutions more efficiently.
Enjoying the daily updates?
Refer your pals to subscribe to our daily newsletter and get exclusive access to 400+ game-changing AI tools.
When you use the referral link above or the “Share” button on any post, you'll get the credit for any new subscribers. All you need to do is send the link via text or email or share it on social media with friends.
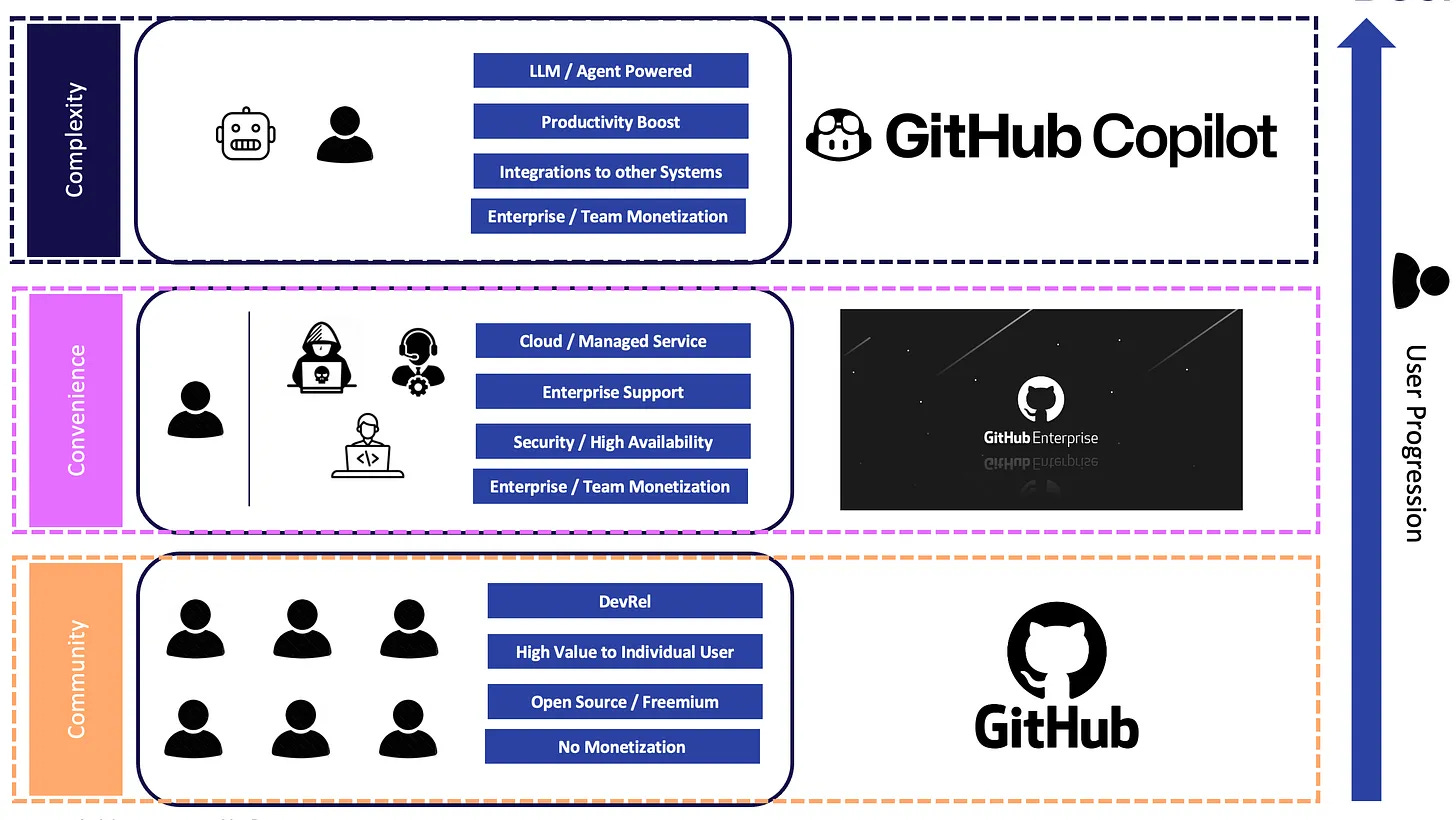
Knowledge Nugget: Defensibility in GenAI: What AI Startups can learn from Github Copilot
In an era that is dominated by a fast-moving incumbent (OpenAI), how can a startup establish a defensible position?
In this article, Dan Nguyen-Huu explores how GitHub Copilot's recent developments, highlighted at GitHub Universe, reveal vital insights for AI startups aiming to build a lasting and successful business. This could include:
Community = 1st-party data, evangelism and adoption: Cultivating and leveraging a robust community of engaged users
Fanatic obsession with UI / UX + AI = User happiness: Focusing intensely on marrying user interface and experience with AI to meet users where they are
Deep integrations into multiple core systems: Developing deeply integrated AI agent systems that provide critical insights and actions across various core systems
Why does this matter?
Despite OpenAI's rapid pace of innovation challenging startups within its ecosystem, the GitHub Copilot has cemented itself as a leader in AI-powered software development tooling. Thus, it offers valuable lessons to forge a long-lasting and defensible position in the fast-evolving world of genAI that necessitates startups to play to their unique strengths.
What Else Is Happening❗
🏁Formula 1 is testing an AI system to help it figure if a car breaks track limits.
Success margins in F1 often come down to tiny measurements. While racers know the exact lines, they sometimes go out of bounds to gain an advantage. To help officials check whether a car's wheels entirely cross the white boundary line, F1 will test an AI system. It won’t entirely rely on AI for now but aims to significantly reduce the number of possible infringements that officials manually review. (Link)
🤚Google Meet’s latest tool is an AI hand-raising detection feature.
Until now, raising your hand to ask a question in Google Meet was done by clicking the hand-raise icon. Now, you can raise your physical hand and Meet will recognize it with gesture detection. (Link)
👩🏫Teachers are using AI for planning and marking, says a government report.
Teachers are using AI to save time by "automating tasks", says a UK government report first seen by the BBC. Teachers said it gave them more time to do "more impactful" work. But the report also warned that AI can produce unreliable or biased content. (Link)
🧬GPT-4’s potential in shaping the future of radiology, Microsoft Research.
A Microsoft research explored GPT-4’s potential in healthcare, focusing on radiology. It included comprehensive evaluation and error analysis framework to rigorously assess GPT-4’s ability to process radiology reports. It found GPT-4 demonstrates new SoTA performance in some tasks and report summaries generated by it were comparable and, in some cases, even preferred over those written by experienced radiologists. (Link)
👗AI can figure out sewing patterns from a single photo of clothing.
Clothing makers use sewing patterns to create differently shaped material pieces that make up a garment, using them as templates to cut and sew fabric. Reproducing a pattern from an existing garment can be a time-consuming task. So researchers in Singapore developed a two-stage AI system called Sewformer that could look at images of clothes it hadn't seen before, figure out how to disassemble them into their constituent parts and predict where to stitch them to form a garment. (Link)
That's all for now!
Subscribe to The AI Edge and join the impressive list of readers that includes professionals from Moody’s, Vonage, Voya, WEHI, Cox, INSEAD, and other reputable organizations.
Thanks for reading, and see you tomorrow. 😊