A New Hack: Stealing Parts of OpenAI Models
Plus: Sakana AI automates foundation model development, Key Stable Diffusion researchers leave Stability AI.
Hello Engineering Leaders and AI Enthusiasts!
Welcome to the 236th edition of The AI Edge newsletter. This edition brings you a new hack to steal parts of black-box models like OpenAI’s models.
And a huge shoutout to our amazing readers. We appreciate you😊
In today’s edition:
🕵️♂️ Stealing Part of a Production Language Model
🤖 Sakana AI’s method to automate foundation model development
👋 Key Stable Diffusion researchers leave Stability AI
📚 Knowledge Nugget: Is translation already dead in the AI era? by
Let’s go!
Stealing Part of a Production Language Model
Researchers from Google, OpenAI, and DeepMind (among others) released a new paper that introduces the first model-stealing attack that extracts precise, nontrivial information from black-box production language models like OpenAI’s ChatGPT or Google’s PaLM-2.
The attack allowed them to recover the complete embedding projection layer of a transformer language model. It differs from prior approaches that reconstruct a model in a bottom-up fashion, starting from the input layer. Instead, this operates top-down and directly extracts the model’s last layer by making targeted queries to a model’s API. This is useful for several reasons; it
Reveals the width of the transformer model, which is often correlated with its total parameter count.
Slightly reduces the degree to which the model is a complete “blackbox”
May reveal more global information about the model, such as relative size differences between different models
While there appear to be no immediate practical consequences of learning this layer is stolen, it represents the first time that any precise information about a deployed transformer model has been stolen.
Why does this matter?
Though it has limitations, the paper motivates the further study of practical attacks on ML models, in order to ultimately develop safer and more reliable AI systems. It also highlights how small, system-level design decisions impact the safety and security of the full product.
Sakana AI’s method to automate foundation model development
Sakana AI has introduced Evolutionary Model Merge, a general method that uses evolutionary techniques to efficiently discover the best ways to combine different models from the vast ocean of different open-source models with diverse capabilities.
As of writing, Hugging Face has over 500k models in dozens of different modalities that, in principle, could be combined to form new models with new capabilities. By working with the vast collective intelligence of existing open models, this method is able to automatically create new foundation models with desired capabilities specified by the user.
Why does this matter?
Model merging shows great promise and democratizes up model-building. In fact, the current Open LLM Leaderboard is dominated by merged models. They work without any additional training, making it very cost-effective. But we need a more systematic approach.
Evolutionary algorithms, inspired by natural selection, can unlock more effective merging. They can explore vast possibilities, discovering novel and unintuitive combinations that traditional methods and human intuition might miss.
Key Stable Diffusion researchers leave Stability AI
Robin Rombach and other key researchers who helped develop the Stable Diffusion text-to-image generation model have left the troubled, once-hot, now floundering GenAI startup.
Rombach (who led the team) and fellow researchers Andreas Blattmann and Dominik Lorenz were three of the five authors who developed the core Stable Diffusion research while at a German university. They were hired afterwards by Stability. Last month, they helped publish a 3rd edition of the Stable Diffusion model, which, for the first time, combined the diffusion structure used in earlier versions with transformers used in OpenAI’s ChatGPT.
Their departures are the latest in a mass exodus of executives at Stability AI, as its cash reserves dwindle and it struggles to raise additional funds.
Why does this matter?
Stable Diffusion is one of the foundational models that helped catalyze the boom in generative AI imagery, but now its future hangs in the balance. While Stability AI’s current situation raises questions about its long-term viability, the exodus potentially benefits its competitors.
Enjoying the daily updates?
Refer your pals to subscribe to our daily newsletter and get exclusive access to 400+ game-changing AI tools.
When you use the referral link above or the “Share” button on any post, you'll get the credit for any new subscribers. All you need to do is send the link via text or email or share it on social media with friends.
Knowledge Nugget: Is translation already dead in the AI era?
In this edition,
features bits of an FT Chinese op-ed authored by a translator who draws on her experience doing English-to-Chinese translation work, providing some fascinating insights into the future of translation in the AI age.It highlights how AI translation tools are impacting the translation profession. While AI can't replace human translators for complex content or nuanced tasks, it can act as a helpful assistant by suggesting phrasing or completing repetitive work. The author also predicts the future of translation will involve human specialists for high-end clients and translators developing new skills to work alongside AI.
Why does this matter?
While the article explores the impact of AI on a specific profession, the discussion about human-AI collaboration and the future of work in translation may offer valuable insights for other sectors that might be grappling with similar questions/changes or other creative or knowledge-based jobs.
What Else Is Happening❗
🗣️Character AI’s new feature adds voice to characters with just 10-sec audio
You can now give voice to your Characters by choosing from thousands of voices or creating your own. The voices are created with just 10 seconds of audio clips. The feature is now available for free to everyone. (Link)
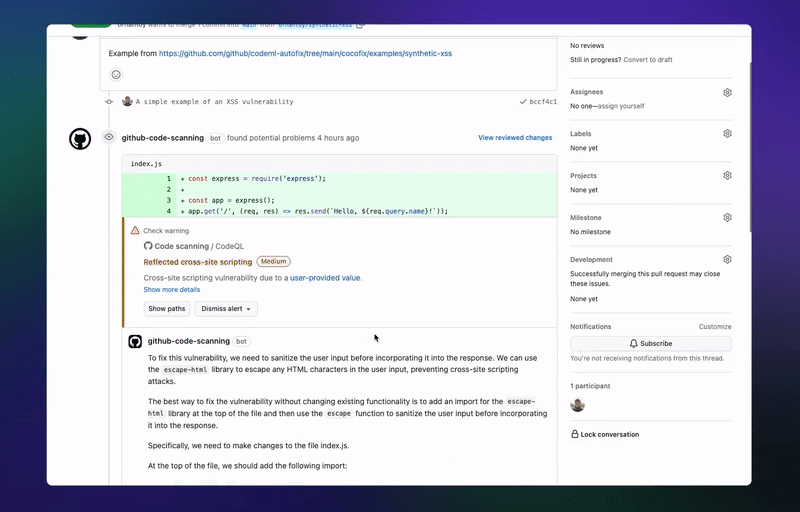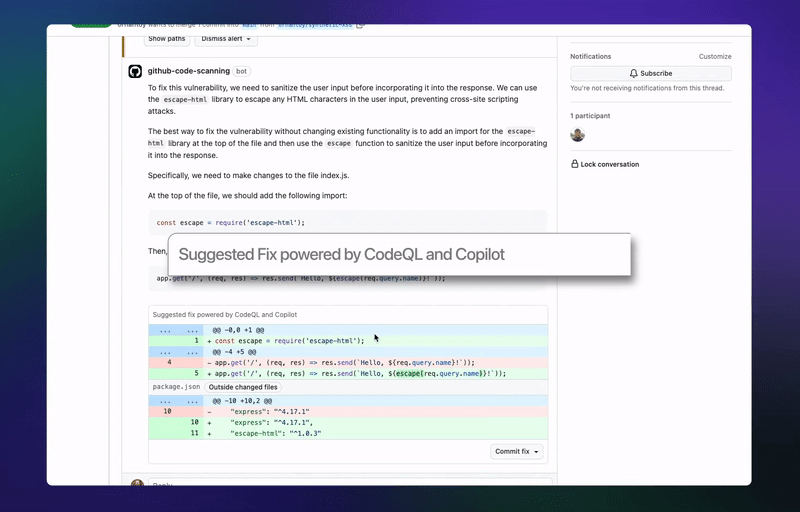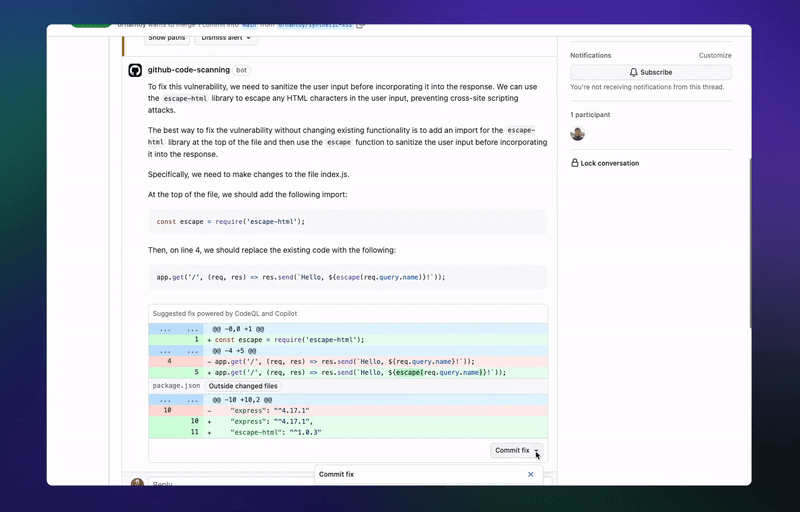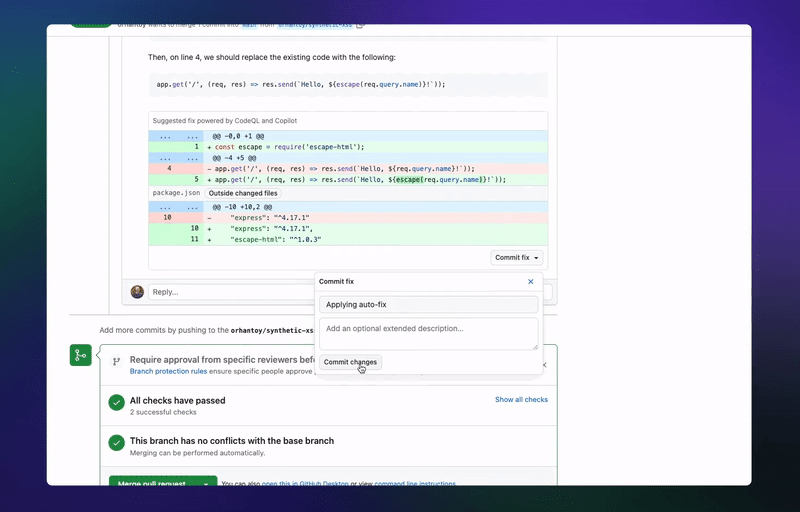
🤖GitHub’s latest AI tool can automatically fix code vulnerabilities
GitHub launches the first beta of its code-scanning autofix feature, which finds and fixes security vulnerabilities during the coding process. GitHub claims it can remediate more than two-thirds of the vulnerabilities it finds, often without the developers having to edit the code. The feature is now available for all GitHub Advanced Security (GHAS) customers. (Link)
🚀OpenAI plans to release a 'materially better' GPT-5 in mid-2024
According to anonymous sources from Businessinsider, OpenAI plans to release GPT-5 this summer, which will be significantly better than GPT-4. Some enterprise customers are said to have already received demos of the latest model and its ChatGPT improvements. (Link)
💡Fitbit to get major AI upgrades powered by Google’s ‘Personal Health’ LLM
Google Research and Fitbit announced they are working together to build a Personal Health LLM that gives users more insights and recommendations based on their data in the Fitbit mobile app. It will give Fitbit users personalized coaching and actionable insights that help them achieve their fitness and health goals. (Link)
🔬Samsung creates lab to research chips for AI’s next phase
Samsung has set up a research lab dedicated to designing an entirely new type of semiconductor needed for (AGI). The lab will initially focus on developing chips for LLMs with a focus on inference. It aims to release new “chip designs, an iterative model that will provide stronger performance and support for increasingly larger models at a fraction of the power and cost.” (Link)
New to the newsletter?
The AI Edge keeps engineering leaders & AI enthusiasts like you on the cutting edge of AI. From machine learning to ChatGPT to generative AI and large language models, we break down the latest AI developments and how you can apply them in your work.
Thanks for reading, and see you tomorrow. 😊